Is Bitcoin Mining Still Profitable?
Analyzing ROI, Electricity, and Equipment Costs
Summary:
Bitcoin mining has evolved from a hobby for early adopters into a highly competitive industry dominated by large-scale Bitcoin farms. With the BTC price surpassing $110,000 in 2025, many investors are asking: is bitcoin mining still profitable? Today, profitability depends on multiple factors including mining hardware, electricity costs, network difficulty, and transaction fees. For those considering entering the market, understanding the economics is essential before committing capital.
How Bitcoin Mining Generates Revenue
Block Rewards & Transaction Fees
As of the latest halving, miners receive 3.125 BTC per block.
Transaction fees now account for a larger portion of earnings, especially during periods of high network congestion.
Mining Pools
Mining pools have become the norm due to increasing network difficulty. Solo mining is impractical for most participants, while pools distribute rewards based on contributed hashrate.
PPS (Pay Per Share): Miners receive a fixed payout for each share of work submitted, regardless of whether the pool finds a block. This provides predictable revenue but may offer lower long-term profits.PPS+ (Pay Per Share Plus): Miners earn the PPS base plus a proportional share of transaction fees from successfully mined blocks, increasing potential earnings during periods of high network activity.Platforms like bitcoin farm tarkov illustrate how both home miners and professionals can leverage pooled mining to secure consistent payouts.
ASIC Bitcoin Miners vs GPU Mining
For BTC mining, ASIC miners outperform GPUs in efficiency and hashpower. Modern ASIC bitcoin miners deliver higher TH/s while consuming less electricity.
Evaluating ASIC Bitcoin miner ROI considering:Cost per terahash (TH), Energy efficiency (watts per TH), Hardware longevity
Older machines lose profitability quickly, while new generation ASIC miner models maintain competitive margins even during network difficulty increases. For serious miners, investing in efficient ASIC Bitcoin miner hardware is critical.
Electricity Costs and Location
Electricity is the largest operational expense in BTC mining. The cost difference between industrial and residential electricity can make or break profitability.
Industrial Electricity: Large-scale Bitcoin farms often secure industrial electricity contracts at rates as low as $0.03–$0.05 per kWh. This low-cost power is a key advantage for professional miners, allowing them to operate high-performance ASIC bitcoin miners while maintaining positive margins.
Residential Electricity: Home miners typically pay $0.10–$0.15 per kWh in many countries, such as the U.S. At these rates, mining profitability drops sharply, making solo or small-scale mining financially unfeasible without access to efficient hardware or pooled mining strategies.
Alternative energy solutions, such as solar, hydro, or capturing flare gas, can reduce operational expenses and improve ROI. Access to cheap, sustainable electricity remains one of the most decisive factors for anyone still mining today.
Calculating Profitability
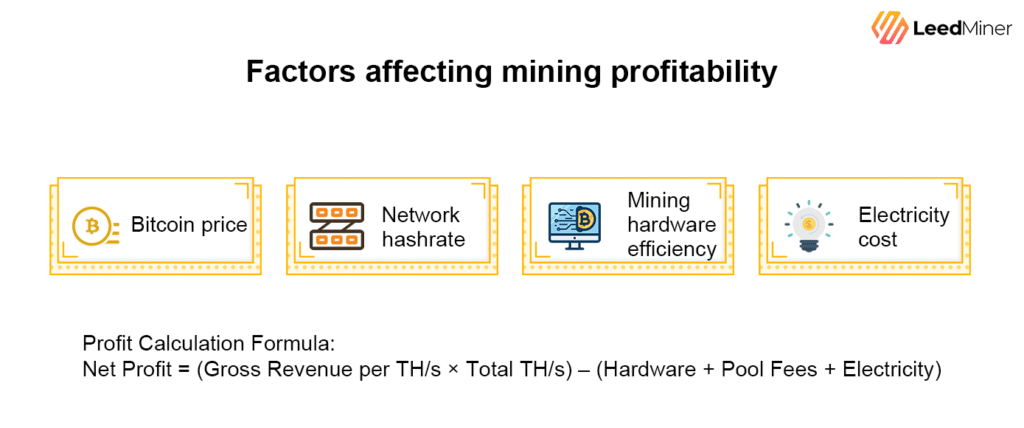
Mining profitability is determined by a combination of:
- Bitcoin price
- Network hashrate
- Mining hardware efficiency
- Electricity cost
Net profit can be approximated as:
Net Profit = (Gross Revenue per TH/s × Total TH/s) – (Hardware + Pool Fees + Electricity)
For those using hashpower marketplaces, the calculation simplifies: users pay for contracts upfront and receive rewards directly, making it easier to model potential ROI before investing.
Timing and Strategy for Maximizing ROI
Effective BTC mining is not passive. Strategic actions include:
Timing Acquisitions: Buy hashpower during anticipated Bitcoin rallies or periods of high transaction fees.
Target Efficient Hashpower: Prefer contracts backed by the latest ASIC miner hardware.
Monitor Network Difficulty: Leverage short-term adjustments in difficulty to increase reward probability.
Adopting an active approach ensures miners can maximize ROI while mitigating exposure to network volatility.
Professional vs Home Miners
Large Bitcoin farms dominate the mining landscape. Their advantages include bulk hardware acquisition, cheap electricity, and advanced operational strategies.
Home miners face steep barriers: higher energy costs, limited access to the most efficient ASIC miners, and lower probabilities of block rewards. Nonetheless, hashpower marketplaces now allow smaller investors to participate in BTC mining without owning physical infrastructure, democratizing access to industrial-scale profitability.
Conclusion: Is Mining Still Worth It in 2025?
BTC mining remains profitable in 2025 for strategic and informed participants. Key factors driving profitability include efficient ASIC miner hardware, low-cost electricity, active management of hashpower, and participation in reliable mining pools.
For individual miners, leveraging hashpower marketplaces or pooling resources provides a practical path to earning Bitcoin while avoiding the high capital requirements of a full-scale farm. The era of passive, set-it-and-forget-it mining is over; success favors agile participants who use data-driven strategies to maximize ROI.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Are home miners at a disadvantage compared to industrial Bitcoin farms?
Are home mining rigs at a disadvantage compared to industrial-grade Bitcoin mining farms?
Industrial-grade Bitcoin mining farms benefit from bulk power contracts, optimized cooling systems, and economies of scale, resulting in lower operating costs and higher long-term profitability.
Home mining rigs typically incur higher residential electricity prices and face limitations in heat dissipation and noise. However, choosing the right home mining rig reveals that this is actually quite simple. There are high-hashrate, low-power home mining rigs on the market that are small, quiet, and require no specialized cooling systems—similar to household appliances. For more details, please refer to another article:Goldshell XT-BOX The Ultimate Home Miner
2. Which ASIC miner is best for Bitcoin mining right now?
The “best” ASIC miner depends on efficiency (J/TH), hash rate, and power cost. In general, newer-generation ASIC bitcoin miners with high energy efficiency provide the strongest ROI. Miners should compare cost per terahash, power usage, and hardware reliability before purchasing.
3. Can someone start mining Bitcoin without buying hardware?
Yes. Hashpower marketplaces and cloud mining platforms allow users to purchase mining power directly instead of owning equipment. This eliminates hardware maintenance and electricity management but requires careful evaluation to avoid overpriced contracts or unreliable providers.
4. How much electricity does a typical ASIC miner use?
A modern ASIC bitcoin miner consumes between 2,000–3,500 watts, depending on the model. The real cost impact depends on local electricity rates:
- Industrial rate: $0.03–$0.06/kWh → typically profitable
- Residential rate: $0.10–$0.15/kWh → often unprofitable without optimization
5. Why do some miners move to colder regions or near power plants?
Cooling and electricity are the biggest operational costs. Colder climates reduce cooling expenses, while proximity to energy sources (hydroelectric, geothermal, stranded natural gas) reduces electricity cost, increasing net profitability.
6. What are some currently popular high-performance Bitcoin mining machines?
Bitmain Antminer S21 Hyd 335Th, Bitmain Antminer S21e XP Hyd 430Th, Bitmain Antminer S19K Pro, These are all high-performance mining rigs, as well as some smaller home mining machines, such as the Goldshell XT-BOX, NerdMiner NerdQaxe++, and Luckyminer series.